You’ve clicked a link or typed a website address. Instead of seeing the page you expected, you’re confronted with a strange message: “403 Forbidden.” Your heart sinks. What does this mean? Did you break something? Is your website in trouble?
Take a deep breath—we’re here to help. A 403 Forbidden Error occurs when a web server understands your request but refuses to fulfill it. It’s essentially a digital “keep out” sign. The server recognizes you’re trying to access something, but it’s programmed to deny that specific request. (Source: MDN Web Docs)
For WordPress site owners, this error can be particularly frustrating. It often appears suddenly and without clear reasons. But don’t worry—in most cases, it’s fixable without deep technical knowledge.
In this guide, we’ll walk through what causes 403 errors, how to identify them, and the simple steps you can take to resolve them. We’ll explain everything in straightforward, non-technical language that anyone can understand.
Understanding the 403 Forbidden Error
The 403 Forbidden Error is part of the HTTP status code family. These codes are like short messages websites send to your browser. Think of them as digital traffic signals that tell your browser what’s happening.
In simple terms, a 403 error means “I understand what you’re asking for, but I’m not allowed to show it to you.” The server recognizes your request is valid but has been configured to deny access to the resource you’re requesting.
This differs from other common errors you might encounter. For example, a 404 error means “I can’t find what you’re looking for,” while a 500 error means “I have an internal problem.
| Error Code | Plain English Meaning | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| 403 Forbidden | “I know what you want but you can’t have it” | Permission issues, security blocks |
| 404 Not Found | “I can’t find what you’re looking for” | Missing pages, broken links |
| 500 Internal Server Error | “I have an internal problem” | Server-side script errors, PHP issues |
| 504 Gateway Timeout | “I took too long to respond” | Server overload, script timeout |
The table above shows how 403 errors compare to other common errors. Each has a distinct cause and meaning, helping you diagnose what’s really happening with your website.
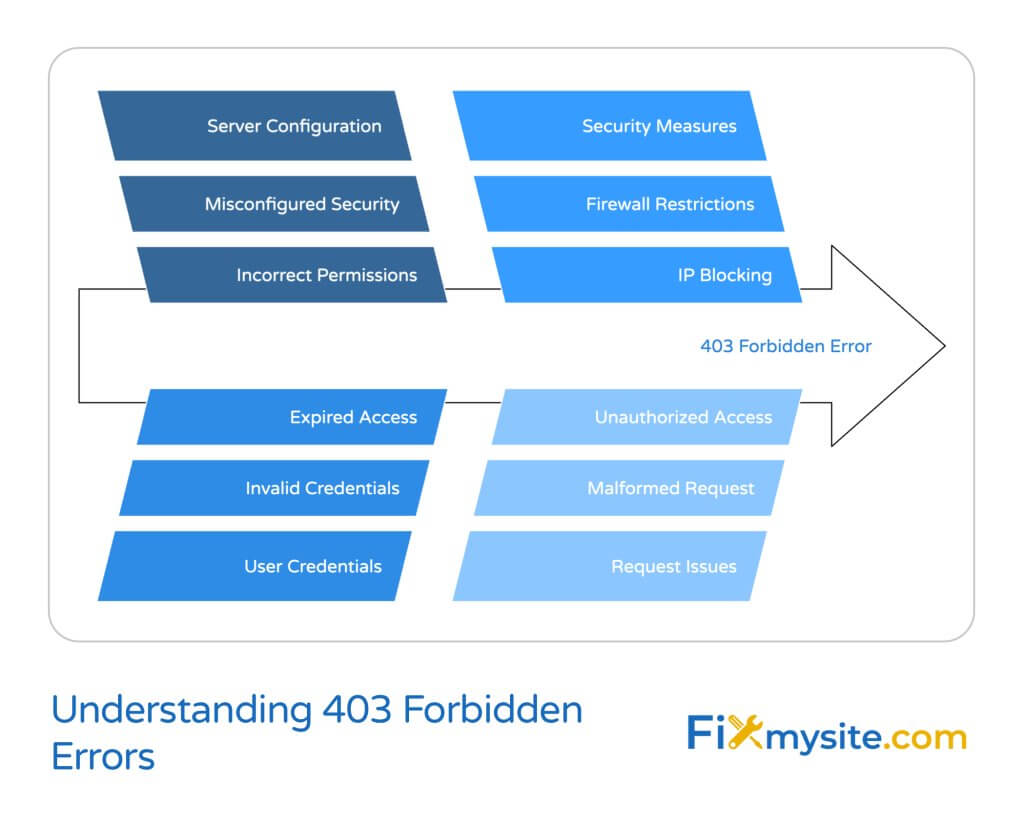
Why does the server “forbid” access? It’s all about permissions and security. Websites are designed with rules about who can access what. When these rules block a request, you see a 403 error.
Think of it like trying to enter a private area without the proper key card. The security system recognizes you’re at the door (your request is valid), but without the right credentials, you can’t enter.
Common Causes of 403 Forbidden Errors
Several issues can trigger a 403 Forbidden Error. Understanding these common causes can help you diagnose and fix the problem more quickly.
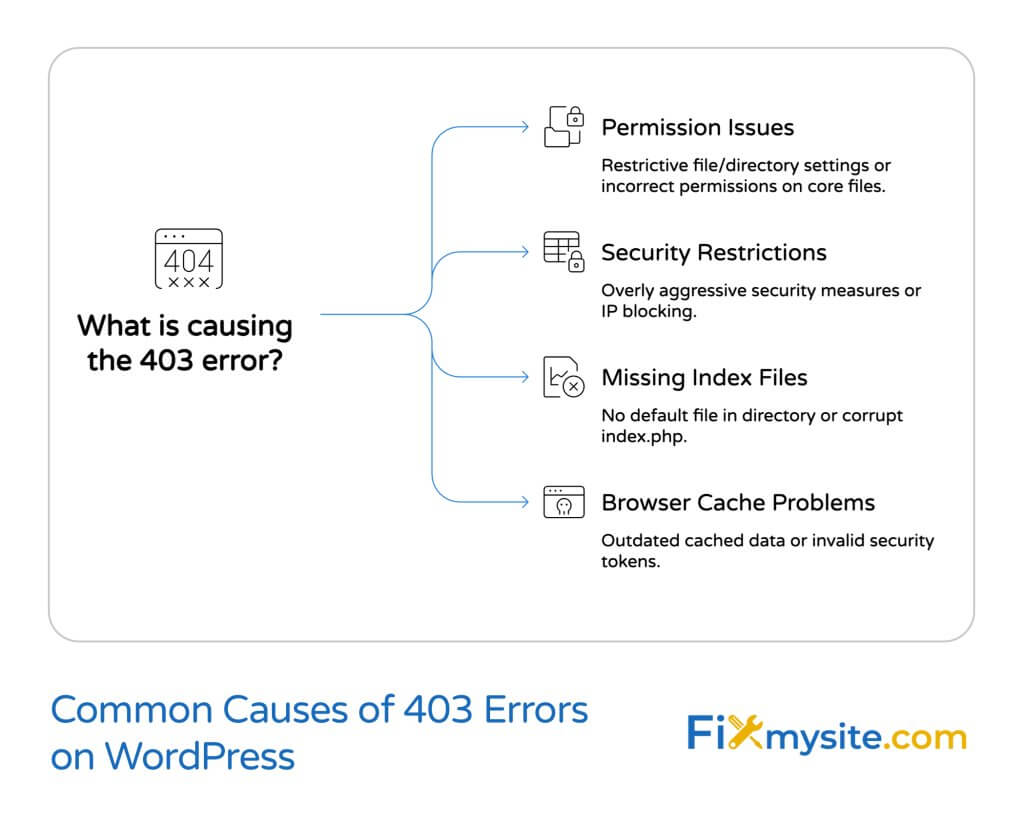
Permission Issues with Files and Directories
The most frequent cause of 403 errors relates to file and directory permissions. Every file on a web server has settings that control who can read, write, or execute it.
If these permissions are too restrictive, the web server can’t access the files needed to display your page. This often happens after making changes to your website or moving to a new host.
In WordPress, this commonly affects core files, themes, or plugin directories. When the permission settings aren’t properly configured, WordPress can’t access what it needs to function correctly.
Security Restrictions and Firewalls
Websites use various security measures to protect against malicious visitors. Sometimes these security systems can be too aggressive and block legitimate users. Security restrictions like IP blocking or firewall rules can trigger 403 errors when they mistakenly identify normal traffic as threatening. (Source: Plesk)
This is particularly common if your site has security plugins installed. Features like brute force protection or country-based access limitations might accidentally prevent access to your own content.
Missing Index Files
Websites typically have a default file (like index.html or index.php) that loads when you visit a directory. If this file is missing or has the wrong name, the server might return a 403 error instead of displaying content. Without an index file, the server doesn’t know what to show when visitors access a directory. (Source: Hostinger)
For WordPress sites, a missing or corrupt index.php file in your main directory or any subdirectory can cause this issue.
Browser Cache Problems
Sometimes the problem isn’t with the website at all but with your browser. Outdated cached data can conflict with what the server expects, resulting in a 403 error.
Your browser stores information about websites you visit to load them faster next time. If permissions or security settings have changed since your last visit, the cached data might no longer be valid.
- File permission issues – Incorrect permission settings on server files
- Security blocks – Firewalls or security plugins blocking access
- Missing index files – Default directory files missing or misnamed
- Cache conflicts – Outdated browser data creating security conflicts
- URL issues – Typos leading to restricted areas of a website
Understanding these common causes can help you narrow down the source of your 403 error and choose the right solution approach.
How to Identify a 403 Forbidden Error
Before fixing a 403 error, it’s helpful to confirm that’s actually what you’re dealing with. Different browsers display this error in slightly different ways, which can sometimes cause confusion.
The 403 Forbidden Error might appear in various formats, depending on your browser, server configuration, or website settings. Here are some common variations you might see:
| Browser | Typical 403 Error Message | Visual Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Chrome | “403 Forbidden” or “Error 403 (Forbidden)” | Simple white page with error text |
| Firefox | “403 Forbidden – Access is denied” | Basic error page with Firefox logo |
| Safari | “403 Forbidden” or “You don’t have permission to access this resource” | Minimalist error page |
| Edge | “403 – Forbidden: Access is denied” | Blue error page with information |
This table shows how different browsers display the same 403 error. The message might vary, but they all indicate the same problem: the server understands your request but won’t fulfill it.
The error message usually includes the number “403” somewhere in the text. You might also see phrases like “access denied,” “forbidden,” or “permission denied.” These all point to the same underlying issue.
In some cases, you might encounter more specific messages like “403 Rate Limit Exceeded” which indicates you’ve made too many requests in a short time period. (Source: Canvas Community)
Sometimes, custom error pages designed by website owners might hide the actual error code. If you suspect a 403 error but don’t see it explicitly stated, look for language mentioning permissions, access rights, or being forbidden from viewing the content.
Simple Troubleshooting Steps for Non-Technical Users
Good news! Many 403 errors can be resolved with simple steps that don’t require technical knowledge. Let’s walk through some easy troubleshooting methods you can try before calling in expert help.
Refreshing the Page
Start with the simplest solution. Refresh the page by pressing F5 or clicking the refresh button in your browser. Sometimes 403 errors are temporary glitches that resolve themselves with a simple refresh.
This works because refreshing forces your browser to make a new request to the server. If the error was caused by a momentary server hiccup or timeout, a fresh request might succeed where the previous one failed.
If refreshing once doesn’t work, try a “hard refresh” by pressing Ctrl+F5 (or Cmd+Shift+R on Mac). This bypasses some cached content and makes a completely fresh request.
Clearing Your Browser Cache
Outdated or corrupted browser cache data is a common cause of 403 errors. Clearing your cache removes old permissions data and forces a fresh connection to the website. (Source: Plesk)
Here’s how to clear your cache in different browsers:
| Browser | Cache Clearing Steps | Keyboard Shortcut |
|---|---|---|
| Chrome | Settings → Privacy and Security → Clear browsing data | Ctrl+Shift+Del |
| Firefox | Options → Privacy & Security → Cookies and Site Data → Clear Data | Ctrl+Shift+Del |
| Safari | Preferences → Advanced → Show Develop menu → Develop → Empty Caches | Option+Command+E |
| Edge | Settings → Privacy, search and services → Clear browsing data | Ctrl+Shift+Del |
After clearing your cache, close your browser completely, reopen it, and try accessing the page again. This simple step resolves many permission-related errors caused by outdated cached data.
Checking for URL Typos
Sometimes a 403 error appears because of a simple typo in the web address. Double-check the URL to make sure it’s exactly correct. Even small errors like missing letters or extra characters can lead to restricted areas of a website. (Source: Microsoft)
Pay special attention to:
- Spelling of domain names and page names
- Use of correct slashes (forward slash / not backslash \)
- Capitalization (some servers are case-sensitive)
- Extra spaces or characters that might have been copied accidentally
If you’re copying a URL from an email or document, try typing it manually instead. This helps eliminate hidden characters or formatting that might cause problems.
Contacting Website Support or Admin
If the steps above don’t resolve the issue, it’s time to reach out for help. For websites you don’t own, contact the site administrator through any available “Contact” or “Help” links.
For your own WordPress site, you might need to contact your hosting provider if you suspect the issue is on their end. When contacting support, be sure to provide:
- The exact URL where you’re seeing the error
- When you first noticed the problem
- Any changes made to your site before the error appeared
- Screenshots of the error message
- Steps you’ve already tried to fix it
This information helps support teams diagnose and solve your problem more quickly. 403 errors are common, and support teams have plenty of experience fixing them.
WordPress-Specific 403 Error Solutions
WordPress websites can experience unique causes of 403 errors. Let’s look at some WordPress-specific solutions that might help fix your issue.
Common WordPress Permission Issues
WordPress requires specific file permissions to function correctly. Sometimes these permissions get changed during updates or file transfers, resulting in 403 errors.
The standard permissions for WordPress files and folders are:
| WordPress Item | Recommended Permission | What It Allows |
|---|---|---|
| Directories/Folders | 755 | Owner can read/write/execute; others can read/execute |
| Files | 644 | Owner can read/write; others can read only |
| wp-config.php | 600 | Only owner can read/write (more secure) |
| .htaccess | 644 | Owner can read/write; others can read only |
If you’re comfortable using an FTP client like FileZilla, you can check and correct these permissions yourself. Otherwise, most hosting providers can help reset permissions to the correct values through their support channels.
Plugin and Theme Conflicts
Sometimes security plugins or poorly coded themes can cause 403 errors. This happens when they incorrectly restrict access to parts of your site.
If your 403 error appeared after installing a new plugin or theme, that might be the culprit. You can troubleshoot by temporarily deactivating plugins one by one to identify which one is causing the problem.
If you don’t have admin access to deactivate plugins normally (because you’re seeing a 403 error), you might need to rename the plugins folder via FTP or your hosting file manager. This effectively deactivates all plugins.
.htaccess File Problems
The .htaccess file controls many access and URL handling rules for your WordPress site. Corrupt or misconfigured .htaccess files are common causes of 403 errors.
If you suspect this is the issue, you can rename the current .htaccess file (to .htaccess.old) and create a fresh one. WordPress will automatically generate a new .htaccess file with default settings when you visit the Permalinks settings page in your admin dashboard.
If you’re experiencing other issues like a broken WordPress theme alongside 403 errors, our guide on how to fix a broken WordPress theme can help with a comprehensive recovery approach.
Need Expert WordPress Help?
403 errors can sometimes indicate deeper WordPress configuration issues. If you’re stuck, our WordPress support experts can quickly diagnose and fix your 403 Forbidden errors, restoring your site with minimal downtime.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many 403 errors can be resolved with the simple steps outlined above, some situations call for professional assistance. Knowing when to call in experts can save you time and prevent further problems.
Consider seeking professional help if:
- The error persists after trying all the troubleshooting steps
- You’ve lost admin access to your WordPress dashboard
- The error affects multiple pages or your entire website
- You recently experienced a security incident or suspect your site was hacked
- You’re not comfortable modifying files or server settings yourself
Before contacting a professional WordPress support service, gather the following information to help them resolve your issue more efficiently:
| Information to Collect | Why It’s Important | How to Obtain It |
|---|---|---|
| Exact error message | Provides specific clues about the cause | Take a screenshot of the error page |
| When the error started | Helps identify triggering events | Note recent changes or updates |
| Affected URLs | Shows the scope of the problem | List all pages showing the error |
| Recent changes | May reveal the root cause | Document recent updates, installations, or settings changes |
This information helps support technicians quickly diagnose the root cause of your 403 error rather than spending time gathering basic details. The more specific information you provide, the faster they can resolve your issue.
Professional WordPress support services like Fixmysite.com specialize in diagnosing and fixing these types of errors. What should you do when your WordPress site is not working? Sometimes the most efficient solution is to have experienced developers investigate the problem.
403 errors related to server configuration or complex permission issues might be beyond what a typical website owner can fix. In these cases, professional help ensures the problem is resolved correctly without creating new issues.

Conclusion
The 403 Forbidden Error can certainly be frustrating, especially when you’re not sure why it’s happening. The good news is that in most cases, it’s fixable—often with simple steps that don’t require technical expertise.
Let’s recap what we’ve learned about 403 errors:
- A 403 Forbidden Error means the server understands your request but refuses to fulfill it due to permission issues
- Common causes include file permission problems, security blocks, missing index files, and browser cache conflicts
- Simple troubleshooting steps include refreshing the page, clearing browser cache, checking for URL typos, and contacting support
- WordPress-specific solutions involve fixing permissions, resolving plugin conflicts, and repairing .htaccess files
If you’ve tried the troubleshooting steps in this guide and still face 403 errors on your WordPress site, it might be time for professional assistance. The ‘This site can’t be reached’ error is another common issue WordPress users face alongside 403 errors.
Understanding WordPress security best practices can help prevent many permission-related errors before they happen.
At Fixmysite.com, we specialize in diagnosing and resolving WordPress errors quickly. Our expert team can fix your 403 Forbidden errors and implement preventive measures to keep your site running smoothly.
Website errors don’t have to be scary or mysterious. With the right approach and support, you can overcome technical challenges and maintain a healthy WordPress site—even without technical expertise.



